This site
is mobile
responsive
Future Forward Economy
Malaysia is actively fostering a future-forward economy, leveraging on its advanced technological landscape among ASEAN nations. Our commitment in embracing modern technologies offers significant advantages to investors. Encapsulated in the Malaysia Digital Economy Blueprint – MyDIGITAL, Malaysia aims to become a digitally driven, high-income nation, and a regional leader in the digital economy. Other key initiatives such as the National Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) Policy, Industry4WRD, Digital Investment Office (DIO), and National Digital Network (JENDELA) also aim to accelerate digital transformation, industry transition, and supply chain optimisation. These digital initiatives work to magnify Malaysia’s global growth potential in the new age.
Our efforts in attracting investments and driving productivity and innovation through economic and regulatory reforms have received worldwide recognition by various international institutions.
Malaysia’s National 4IR Policy builds upon Industry4WRD framework, aiming to drive comprehensive transformation and ethical use of 4IR’s technologies for the country’s socioeconomic development.
The National 4IR Policy is aligned with MyDIGITAL Blueprint and also the National Policy on Science, Technology and Innovation (DSTIN) 2021-2030 that aims to develop Malaysia as a high-tech nation by 2030.
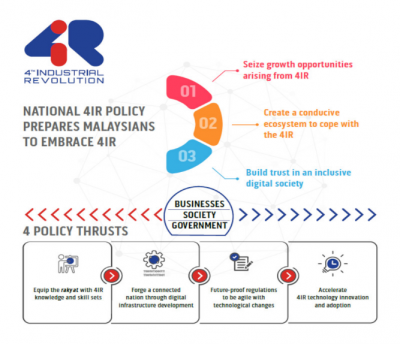
The National 4IR policy promotes policy coherence for sustainable resource optimisation and implementation coordination, aligned with Malaysia’s Shared Prosperity Vision 2030 and commitment to Sustainable Development Goals.
To expedite technology adoption and foster local innovation, the National 4IR policy aims to create a favourable ecosystem in terms of talent, infrastructure, regulation, and technological capability.
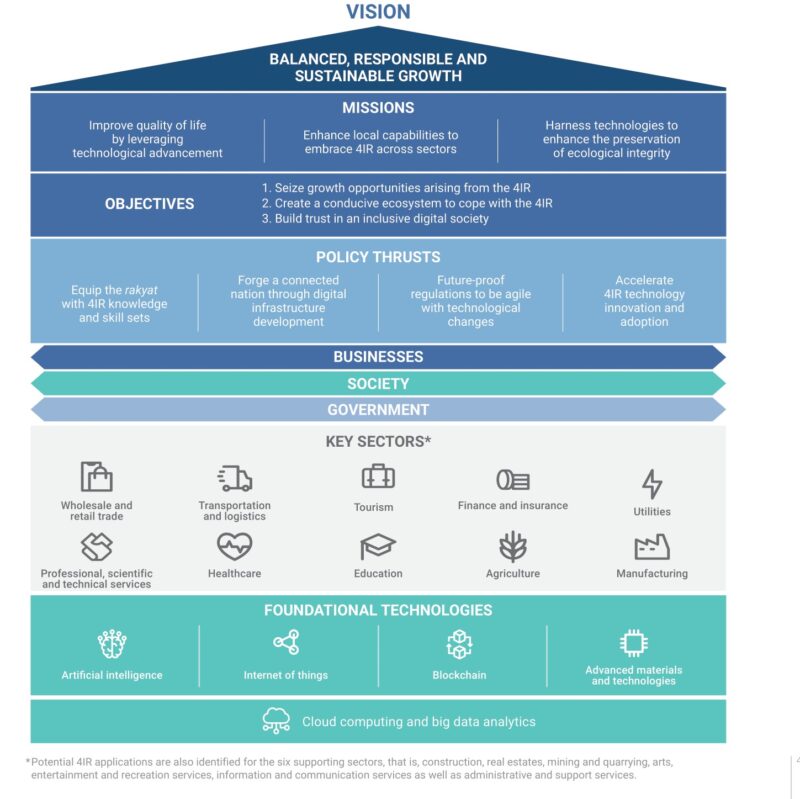
Source: Ministry of Economy

Malaysia’s Industry4WRD policy drives the transformation of the manufacturing sector, integrating people, processes, and technology. It represents the country’s strategic shift towards embracing Industry 4.0, paving the way for smart manufacturing and the eventual development of smart cities, grids, and solutions.
Malaysia is actively embracing Industry 4.0, elevating its industrial capabilities up the value chain to establish itself as a premier global industrial hub. A key focus is placed on enhancing technical and vocational education and training (TVET) to bridge the skills gap and nurture a workforce ready for the demands of the industry.
In Malaysia, businesses and government agencies collaborate to bridge the talent gap. The Malaysia Education Blueprint anticipates a demand for 1.3 million more TVET employees. To tackle this, MIDA, in partnership with the Federation of Malaysian Manufacturers (FMM) and the Ministry of Education (MOE), has introduced an Apprenticeship Programme.
These goals and targets align with Malaysia’s national vision to transform the manufacturing industry – driving performance improvement, technological advancement, skill development, and workforce expertise – with the aim to increase the sector’s contribution to the economy at large.

MIDA welcomes Tesla – a leading American multinational electric automotive manufacturer – with its strategic expansion into the Malaysian market. This expansion is a direct response to the Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Global Leaders initiative introduced by the Ministry of Investment, Trade and Industry (MITI). Tesla’s operation in Malaysia will involve Vehicle Importation, Supercharger Network, Head Office & Service Centre, and Experience Centre.
MIDA has approved 58 projects totalling RM26.2 billion in the EV and its related ecosystems from 2018 to March 2023. The approved investments span various areas, including EV assembly, manufacturing of EV parts and components as well as its charging components. As the demand for sustainable transportation continues to rise, MIDA’s support and facilitation of these projects contribute to the advancement of the EV sector in Malaysia, fostering economic development, job creation, and a greener future.
With its steadfast commitment to innovation, sustainability, and customer satisfaction, Tesla is primed to revolutionise the Malaysian automotive market and contribute significantly to the nation’s environmental goal to become carbon neutral by 2050, in alignment with Malaysia’s pledge to reduce carbon emissions under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).

We are pleased that Tesla has chosen Malaysia as one of its destinations for their expansion in Southeast Asia. Their commitment to sustainable mobility is closely aligned with Malaysia’s vision for a greener future, and our New Industrial Master Plan 2030’s push for net zero. MITI is focused on transforming our industrial and investment landscape to not only attract companies like Tesla to help enhance our domestic suppliers’ position in global value chains but also open up new ‘greener’ economic opportunities and create higher-paying jobs for Malaysians. Tesla’s presence here will also help raise Malaysia’s pro-business and pro-investment credentials on the global stage, and we look forward to welcoming more multinational investors that share our vision of developing a more sustainable, balanced, and inclusive economic growth for our nation.
– YB Tengku Datuk Seri Utama Zafrul Aziz, Minister of Investment, Trade and Industry, MITI (2023)
The increased efficiency in the sector and enhanced development capacities are transforming Malaysia into a leading provider of advanced technology services.
The Digital Free Trade Zone (DFTZ) combines physical and digital zones to support SMEs in capitalising on the exponential growth of the web economy and cross-border e-commerce. It expands Malaysia’s e-commerce roadmap, aiming to increase e-commerce growth and its GDP contribution to RM211 billion (US$48 billion) per year.
Under the National e-Commerce Strategic Roadmap, MIDA has been entrusted as the lead agency responsible for facilitating Malaysia’s transformation into a renowned regional e-fulfilment hub.
DFTZ aims to:
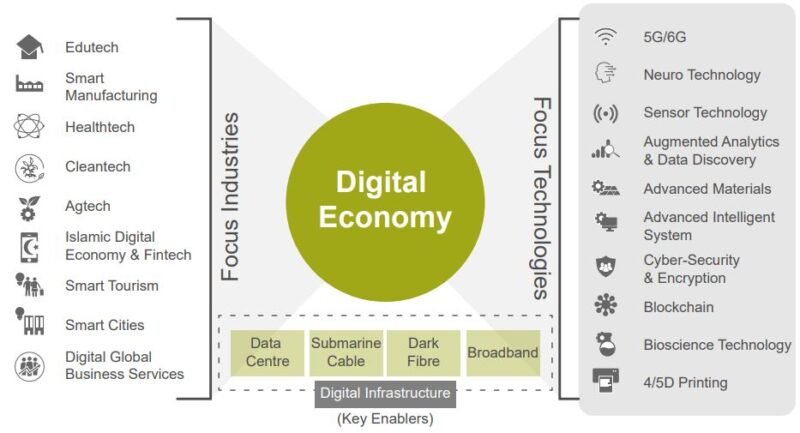
Launched in 2020, Jendela is a RM21 billion national digital infrastructure plan designed to steer Malaysia towards greater digital connectivity by boosting the efficiency of the national infrastructure and optimising spectrum usage. The plan aims to provide the foundation for comprehensive and quality broadband coverage, and prepare the country to adopt the 5G technology.
Explore how 5G in Malaysia can unlock innovation and new opportunities. As part of MyDIGITAL initiative, a total of RM15 billion will be invested over a period of 10 years to facilitate the nationwide rollout of 5G.
The Government is encouraging the development of a reliable 5G ecosystem and promoting its adoption in industries and the public sector, including automotive, manufacturing, education, agriculture, tourism, and media.
MyDigital Blueprint (2021-2030) spearheads digital economy growth through its initiatives, key strategies, and ambitious targets. Key objectives entail a RM70 billion investment in digitalisation, increased number of start-ups to 5,000, driving a 30% productivity surge across sectors, and propelling the digital economy to contribute 22.6% to Malaysia’s GDP.
The National Council of Digital Economy and Fourth Industrial Revolution (MED4IR) chaired by the Prime Minister endorsed the establishment of the Digital Investment Office (DIO) which is entrusted to charge towards facilitating digital investments in Malaysia. The role of DIO is consistent with MyDIGITAL and the National Investment Aspirations, guided by the essence of the Shared Prosperity Vision (SPV) 2030.
The DIO is a fully digital collaborative platform between MIDA, and the Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) designed to coordinate and facilitate digital investments. This initiative aims to enhance awareness of digital investment in the country and improve coordination among Investment Promotion Agencies (IPAs) to attract and promote new investments in this fast-evolving segment.
For further enquiries, please click here.

IDI2023, which measured 10 indicators, reported that Malaysia has, among others achieved near-universal coverage of 4G or LTE mobile networks, high mobile-broadband subscriptions and affordable prices for mobile and fixed-broadband services.
— The ICT Development Index (IDI) 2023