
This site
is mobile
responsive
Tourism is the third-largest contributor to Malaysia’s GDP, after the manufacturing and commodities sectors. In 2019, the sector contributed about 15.9 per cent to the total GDP. In the last few years before the outbreak of COVID-19, the tourism industry in Southeast Asia had experienced a significant growth phase, and Malaysia launched the “Visit Truly Asia Malaysia 2020” campaign with a target of 30 million visitors and RM100 billion in tourist revenue for 2020. However, the COVID-19 outbreak severely impacted the Malaysian tourism industry, which led to the cancellation of the campaign.
The Government then launched the National Tourism Policy (NTP) 2020-2030 on 23 December 2020 to ensure the continuity of the country’s tourism industry and make Malaysia a preferred tourist destination globally. Key approaches in achieving the NTP’s agenda include effective recovery of the tourism industry based on new norms, strengthening competitiveness, sustainable and inclusive tourism development, as well as disaster risk management.
Among the Transformation Strategies outlined in the NTP is to embrace ‘Smart Tourism’. Advances in digital technology have influenced the way people travel, causing tourism-related businesses to change the way they operate.
The Malaysia Smart Tourism 4.0 initiative launched by Tourism Malaysia on 5 April 2018 aims to take the industry to the next level by taking advantage of opportunities in the digital age. These efforts will pave the way for new innovative sub-sectors and create employment opportunities in line with the NTP and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). In a study conducted by Monitor Deloitte, ‘Smart Tourism’ has the potential to increase Malaysia’s tourism-based revenues from the current USD25 billion to USD110 billion by 2030, an increase of more than 4-fold.
According to Dr Hayley Stainton, the founder and CEO of Tourism Teacher, “Smart Tourism is defined according to the technological capabilities of a particular destination, attraction or the tourist themselves.”
The definition is supported by The European Capital of Smart Tourism which defines a smart destination as:
‘A destination facilitating access to tourism and hospitality products, services, spaces and experiences through ICT-based tools. It is a healthy social and cultural environment, which can be found through a focus on the city´s social and human capital. It also implements innovative, intelligent solutions and fosters the development of entrepreneurial businesses and their interconnectedness.’
The ultimate aim of smart tourism is to improve resource management efficiency, enhance tourism experiences, maximise competitiveness, and enhance sustainability through technological innovation and practices.

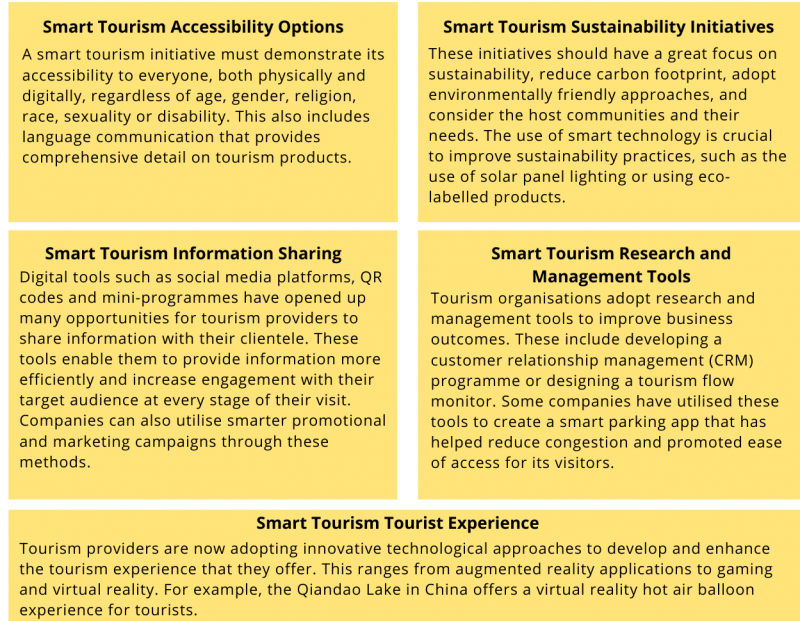
The five most common methods of implementing smart tourism
While the tourism sector has taken a hard blow due to the pandemic, the focus on digitalisation and developing smart products and infrastructure are among initiatives to build a more resilient and sustainable future in Malaysia. Taking a positive spin, a crisis is often an opportunity to rethink and reinvent old processes, particularly to adopt more sustainable tourism practices. According to UNWTO (UN World Tourism Organisation), sustainable tourism ‘has the potential to advance urban infrastructure and universal accessibility, promote the regeneration of damaged areas and preserve cultural and natural heritage, assets that depend on tourism’.
In recent years, there has been a demand for high-class hotel development in response to the increase in global wealth and higher living standards among developed and developing countries. The upcoming mega projects and large mixed-use development in TRX, Bandar Malaysia and KL Metropolis are expected to attract upperupscale and luxury hotels. It is estimated that the proposed investment for the establishment of 4 and 5 star hotels in Malaysia amounted to RM7 billion in 2021.
In efforts to develop Malaysia’s tourism landscape into a sustainable, competitive and resilient sector, incentives are provided to encourage existing operators of 4 and 5-star hotels and smart tourism. MIDA welcomes quality investments that involve high-value and innovative tourism products and services, and contributes to a comprehensive ecosystem such as special tourism investment zones without compromising on environmental policies and legal requirements. MIDA also encourages companies to invest in modern and higher standard infrastructure and facilities to build up the resilience and long term competitiveness of the tourism sector.